Özmen S.
Lung , Jefree J. Schulte,M.D., Editör, Pthology Outlines, Michigan, ss.1, 2023
-
Yayın Türü:
Kitapta Bölüm / Ders Kitabı
-
Basım Tarihi:
2023
-
Yayınevi:
Pthology Outlines
-
Basıldığı Şehir:
Michigan
-
Sayfa Sayıları:
ss.1
-
Editörler:
Jefree J. Schulte,M.D., Editör
-
Atatürk Üniversitesi Adresli:
Evet
Özet
Lung
Adenocarcinoma
Enteric
Last author update: 21 March 2023
Last staff update: 21 March 2023
Copyright: 2022-2024, PathologyOutlines.com, Inc.
PubMed Search:
Enteric adenocarcinoma lungPage views in 2023: 5,867
Page views in 2024 to date: 400
Cite this page: Özmen S, Oltulu P. Enteric. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumoradenoenteric.html. Accessed January 23rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Pulmonary enteric adenocarcinoma (PEAC) is an extremely rare subtype of non-small cell lung cancer that is characterized by pathological features similar to those of colorectal adenocarcinoma
Terminology
- Adenocarcinoma, enteric type
- Primary lung enteric adenocarcinoma
- Pulmonary intestinal type adenocarcinoma (not recommended)
- Pulmonary adenocarcinomas showing enteric differentiation (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8144/3 - adenocarcinoma, intestinal type
- ICD-10: C34 - malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung
- ICD-11: 2C25.0 & XH0349 - adenocarcinoma of bronchus or lung & adenocarcinoma, intestinal type
Clinical features
- Clinical features are not substantially different from those of other lung adenocarcinomas
- Most patients are elderly men and smokers with advanced stage disease (Hum Pathol 2017;64:179, Exp Ther Med 2016;11:201, Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8153)
- Nonproductive cough and chest pain, fever, hemoptysis (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1266)
- Compared with primary pulmonary invasive adenocarcinoma, patients with PEAC are older and have larger lesions at more advanced stages (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8153)
- Coughing is the most common but nonspecific symptom (Chin Med J (Engl) 2019;132:1368, Oncol Lett 2017;13:4651)
- Other symptoms include expectoration, hemoptysis, chest tightness, chest pain, shortness of breath, fever, night sweats, throat discomfort, headache, fatigue and enlarged cervical lymph nodes (Chin Med J (Engl) 2019;132:1368)
- lt is crucial to exclude metastatic colorectal carcinoma, which is more common than primary enteric type adenocarcinoma in the lung, by careful clinical evaluation (Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29:660)
- No gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., hematochezia, nonproductive abdominal pain, diarrhea and ventosity) (Transl Oncol 2021;14:101123, ScienceDirect: Gastrointestinal Distress [Accessed 21 March 2023], ScienceDirect: Rectal Bleeding [Accessed 21 March 2023])
Diagnosis
- Tumor with enteric morphology and expression of intestinal markers (CDX2, CK20, HNF4a or MUC2) and coexpression of TTF1 or CK7
- Considering the common clinical features with other adenocarcinomas, a combination of clinical signs, histopathology, IHC and molecular features is required for a definitive diagnosis
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma should be ruled out by endoscopy and radiology, even if the pathological results correspond to primary enteric adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Pathology and immunohistochemistry results are mostly used in the diagnosis of PEAC (World J Clin Cases 2021;9:9236)
- The patient can finally be diagnosed with PEAC when primary PEAC consists mainly of tissue with > 50% intestinal differentiation, tumor cells are positive for at least 1 immunohistochemical marker associated with colorectal cancer (e.g., CK20, CDX2, MUC2, villin, etc.) and tumors of gastrointestinal origin are excluded
- CK7 is important for pulmonary origin
Radiology images
Images hosted on other servers: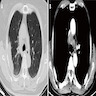
Right upper lobe
and mediastinal
lymph node
metastasis
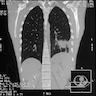
Tumor in the lower lobe of the left lung
Treatment
- Current treatment strategy is the same as for primary adenocarcinoma
- A comprehensive treatment supported by surgical treatment, chemotherapy, radiotherapy or targeted therapy is selected according to clinical stage (Transl Oncol 2021;14:101123, World J Clin Cases 2021;9:9236)
- Patients may benefit from anti-HER2 therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors (Transl Oncol 2021;14:101123)
- EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor in PEAC is unreasonable and inefficient (J Transl Med 2018;16:81)
- Patients may be more likely to benefit from checkpoint blocking immunotherapy (J Transl Med 2018;16:81)
- Although only limited data are available, alterations eligible for tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy seem to be less common than in other non-small cell lung cancer subtypes (Mod Pathol 2019;32:855)
Frozen section description
- An adenocarcinoma with enteric morphology may be said to be present on frozen sections but without immunohistochemical study and radiological and clinical correlation, it cannot be determined whether the malignancy in the lung is primary or secondary
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Enteric pattern exhibits the features of colorectal adenocarcinoma, which has glandular, papillary or cribriform structures with luminal necrosis, tall columnar cells with pseudostratified and atypical nuclei, and eosinophilic cytoplasm (Oncol Lett 2017;13:4651, Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1266)
- Enteric pattern can be admixed with other patterns of adenocarcinoma
- Mitotic figures are often found
- Stroma is often desmoplastic and associated with prominent inflammatory cell infiltrates
- Histologically, PEAC has features of intermediate differentiation and sometimes forms a cribriform pattern with tall columnar cells arranged in irregular acini or with extensive central necrosis (Oncotarget 2017;8:63442)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Sevilay Özmen, M.D. and Pembe Oltulu, M.D.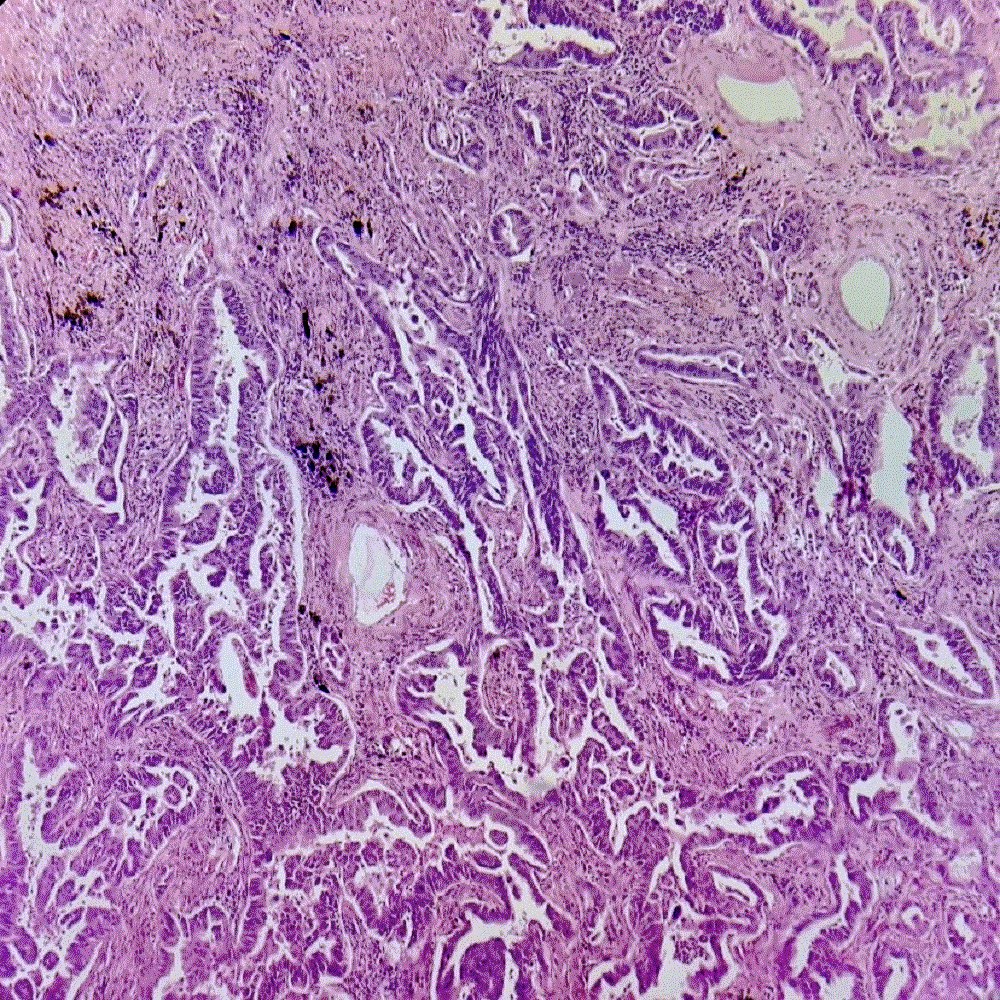
Moderately differentiated glands with necrotic debris
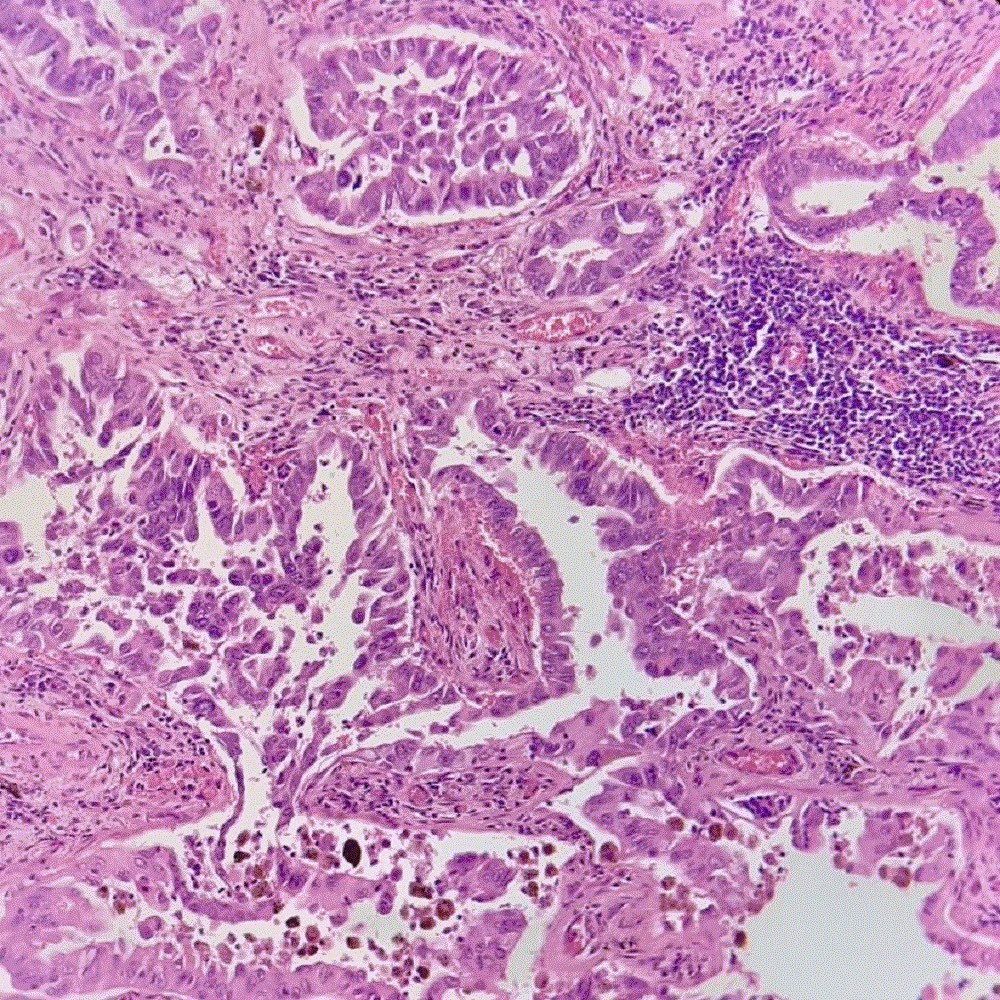
Cribriform and acinar growth pattern
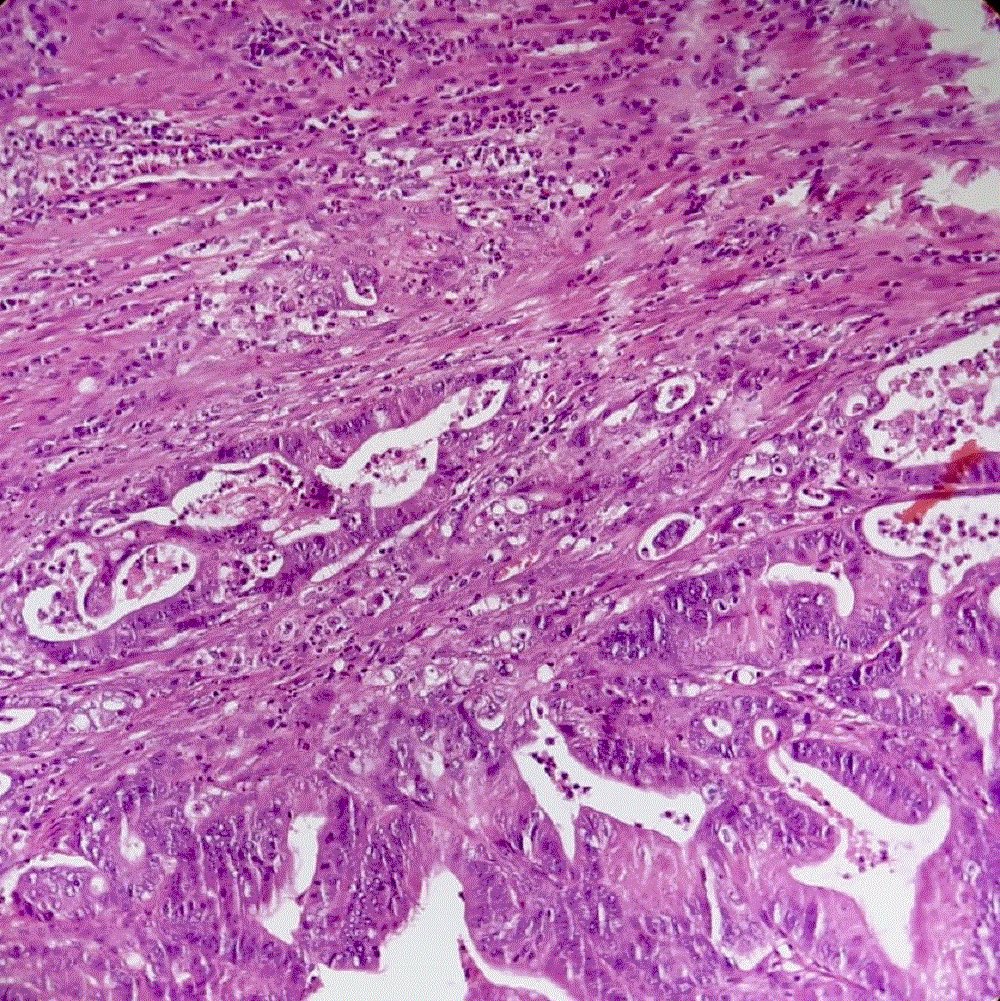
Glands filled with necrotic debris
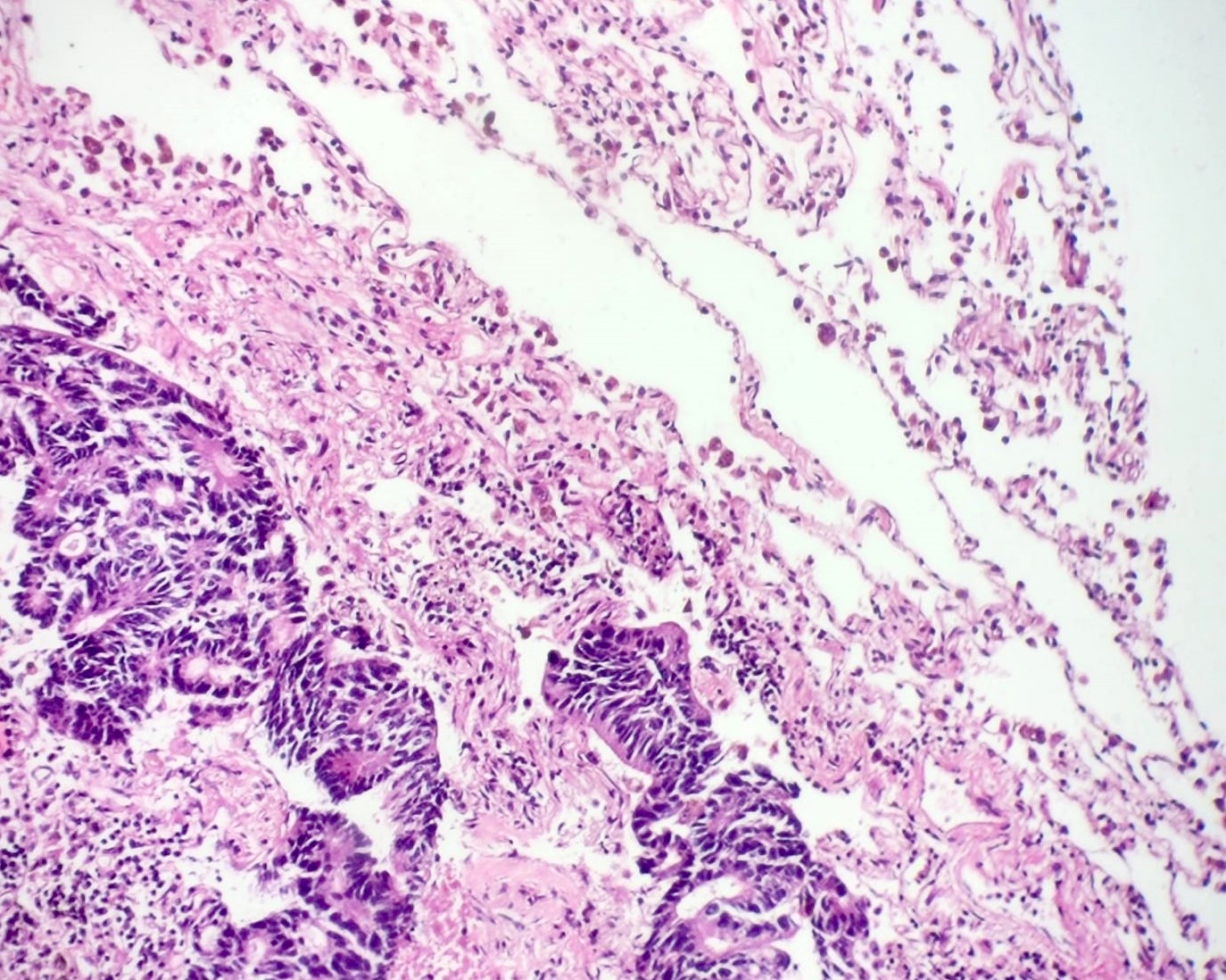
Cribriform growth pattern
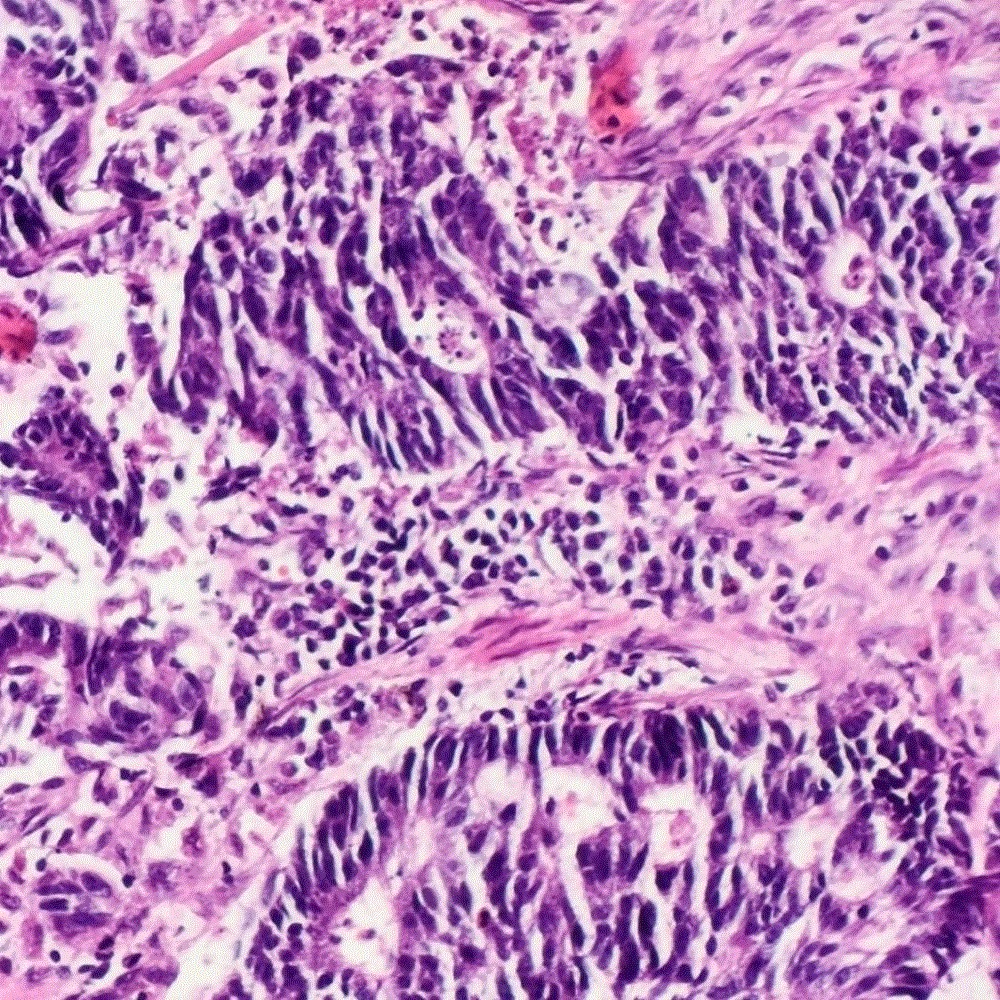
Glands filled with necrotic debris
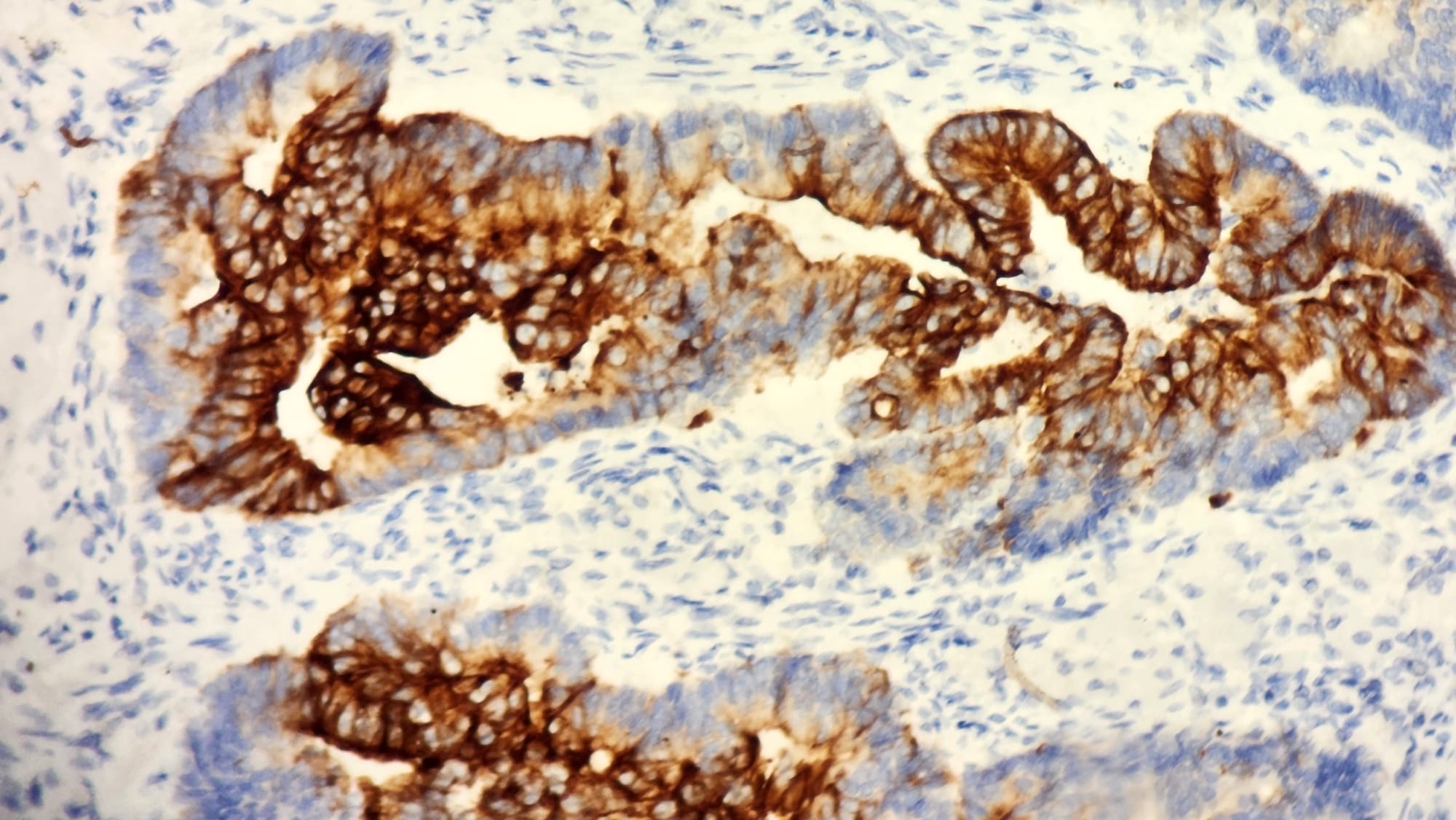
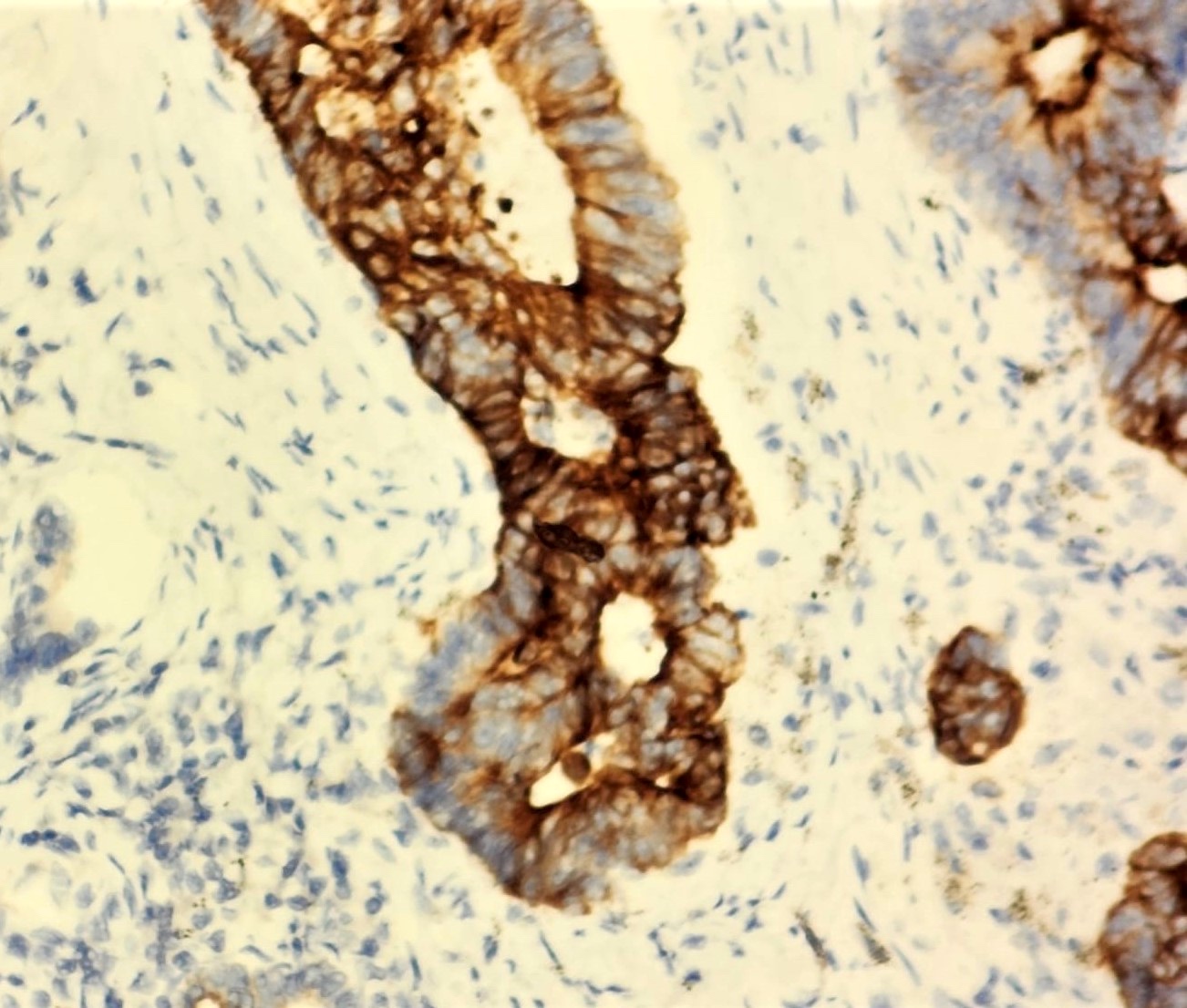
CK7 positivity
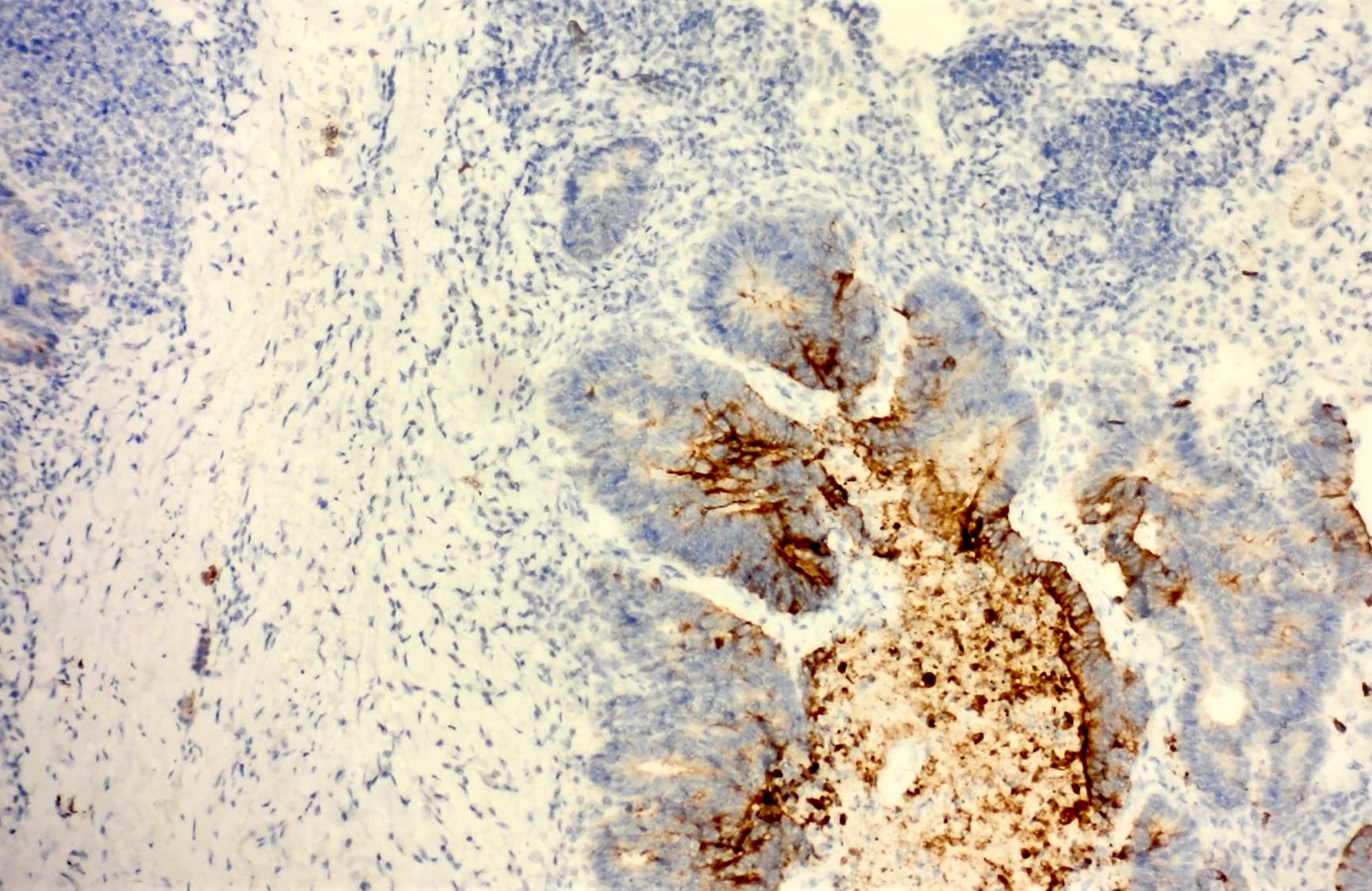
CK20 positivity
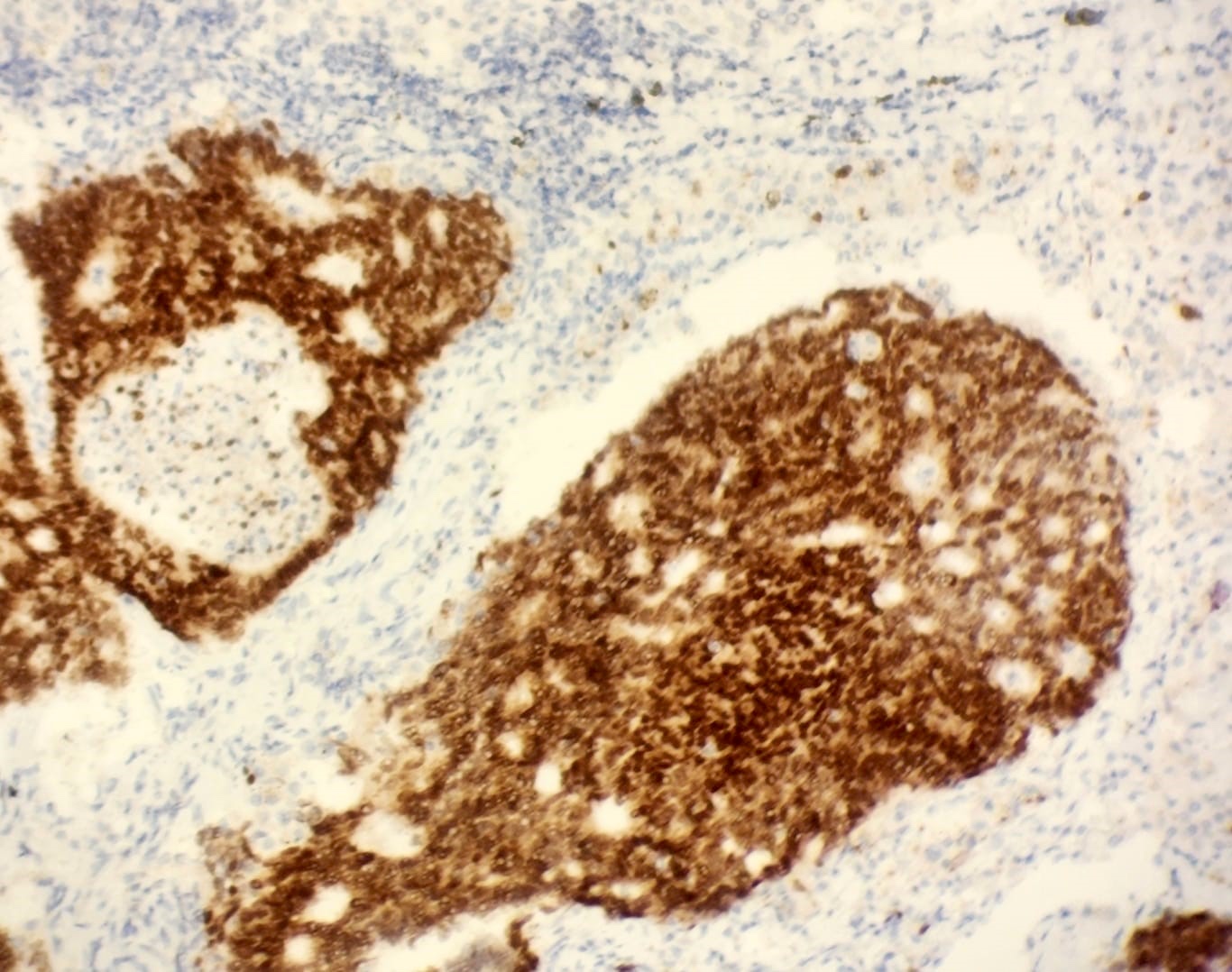
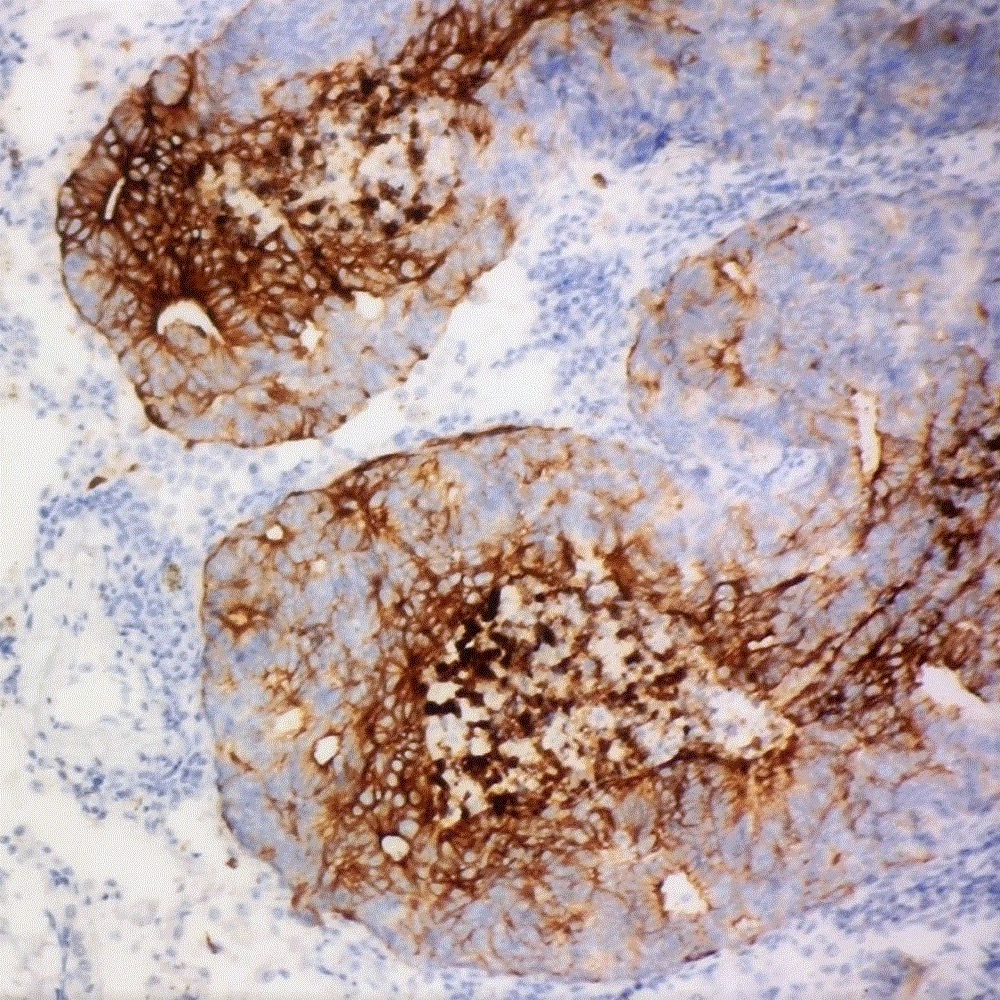
CDX2 positivity
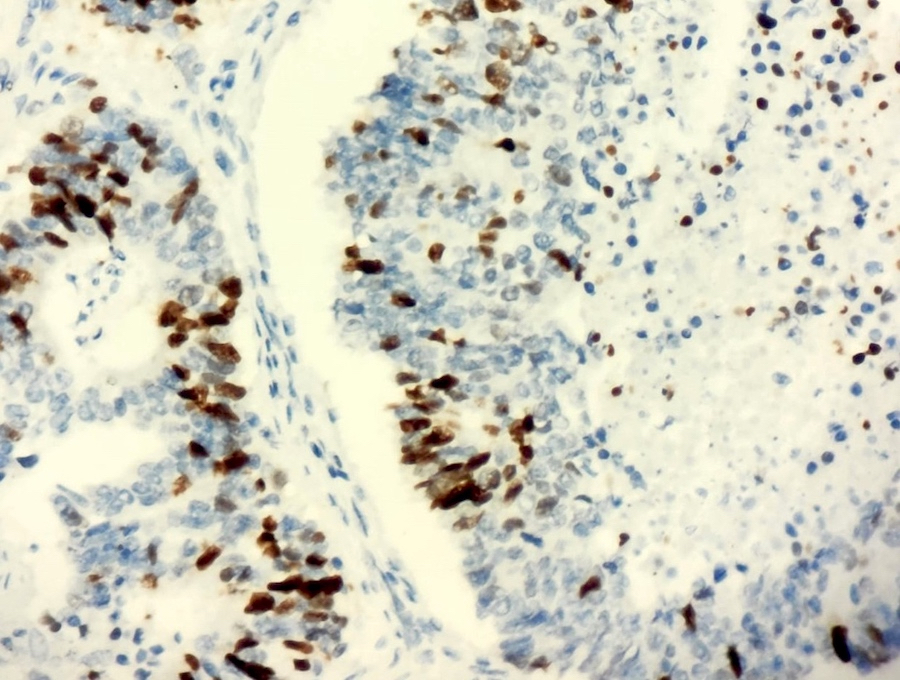
TTF1 positivity
Cytology description
- Sheets or papillary clusters of high columnar cells
- Intracytoplasmic mucin
Cytology images
Contributed by Sevilay Özmen, M.D.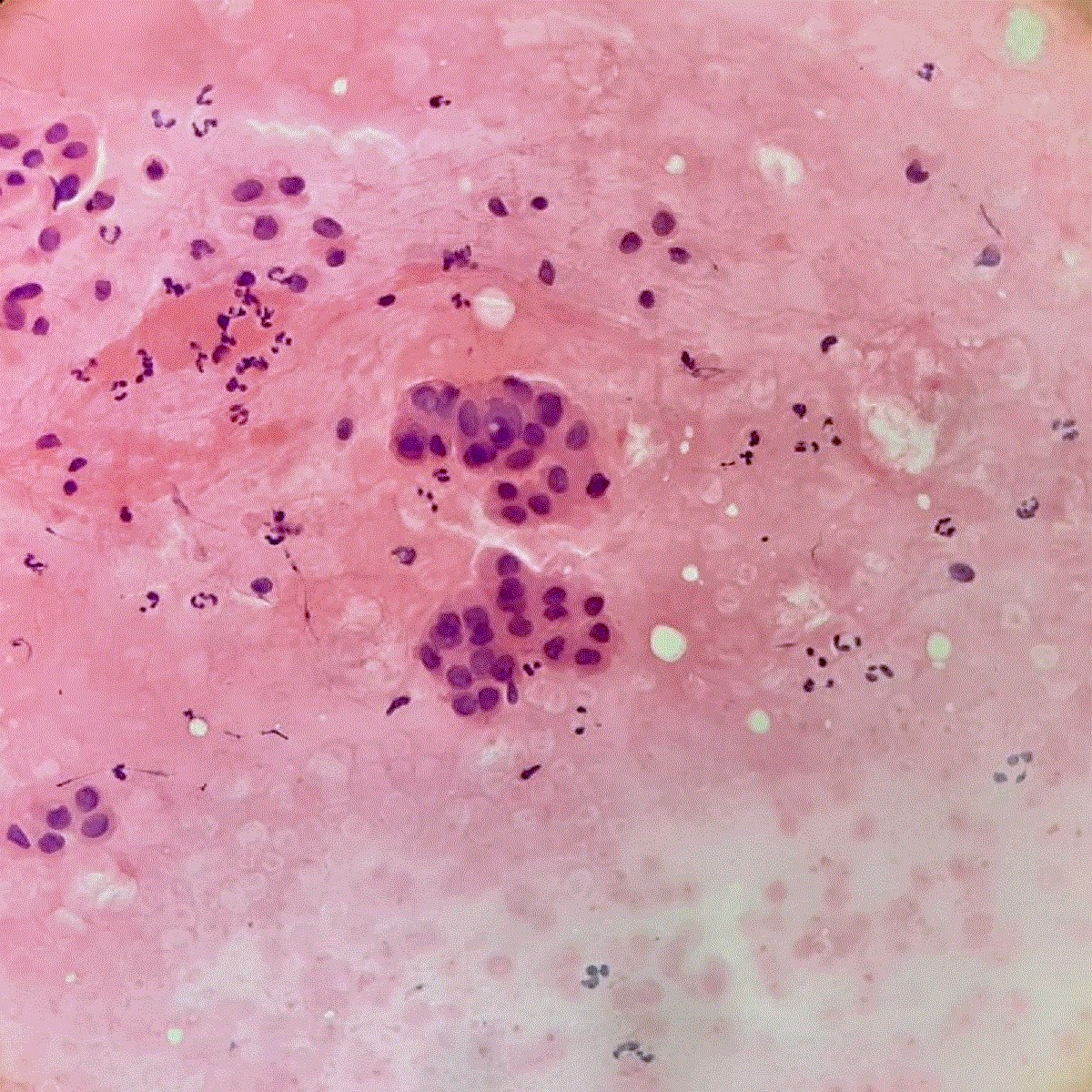
Small clumps of tumor cells
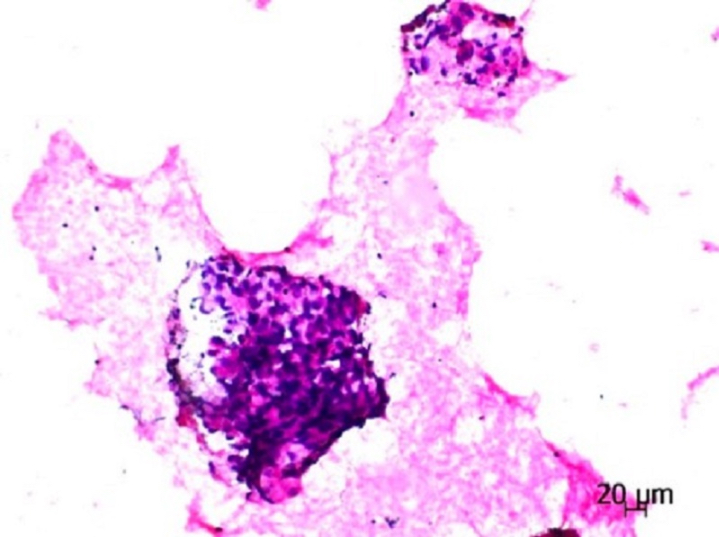
Cluster of tumor cells
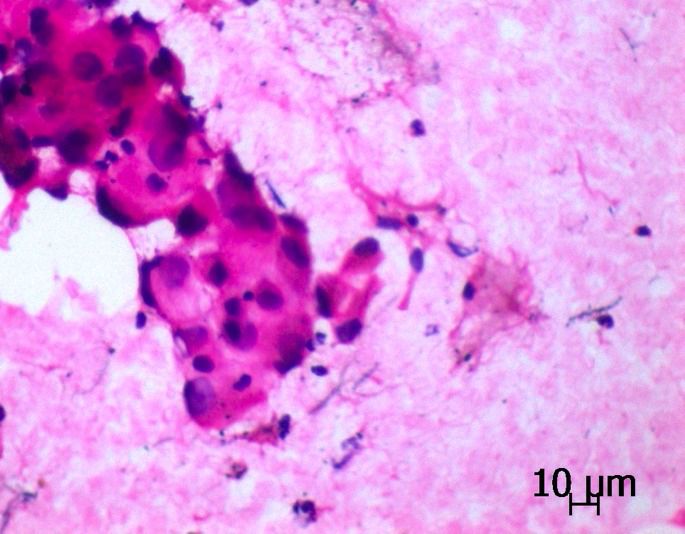
Papillary cluster
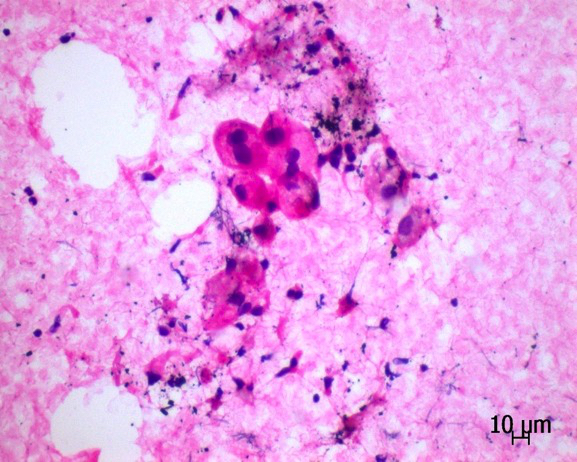
Acinar cluster
Molecular / cytogenetics description
Sample pathology report
- Lung, right upper lobe, resection:
- Pulmonary enteric adenocarcinoma (see synoptic report)
- Lung, biopsy:
- Adenocarcinoma with enteric differentiation (see comment)
- Comment: In the case where malignancy in the gastrointestinal tract was excluded, the findings are consistent with enteric differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Board review style question #1
What gene mutation is most commonly associated with enteric adenocarcinoma?
- BRCA
- EGFR
- KRAS
- NRAS
- PIK3CA
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
A 60 year old man presented with complaints of cough, chest tightness and shortness of breath. He was a former smoker with 20 pack years. Chest tomography showed a 6 cm mass in the periphery of the lung. A biopsy was performed. Tumor cells immunohistochemically express CK7, CK20, CDX2 and TTF1 and the patient does not show malignancy in the gastrointestinal tract. According to the image above, what is the pathological diagnosis?
- Adenocarcinoma with enteric differentiation
- Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung
- Large cell carcinoma of the lung
- Small cell lung cancer
- Squamous cell lung cancer
Board review style answer #2